Eleven Software Announces Acquisition of Airangel

Enhance customer loyalty and empower guests with fast, secure, reliable connectivity.








Connect guests and devices for a brilliant Wi-Fi experience. Guests and residents take their Wi-Fi everywhere on the property.
Our centralized dashboard enables network management in real time. You can also configure service plans, manage group access, onboard IoT devices, and more.
Deliver branded Wi-Fi that exceeds expectations across your portfolio. Connect ElevenOS to your PMS, CRM or loyalty programs to boost ROI with your Wi-Fi amenity.
Don’t sweat the tech. With ElevenOS integrations, you can enjoy superior functionality without the hassle of adding or replacing hardware. Our system integrates with mobile app servers, PMS systems, CRMs, and more so you can deliver world-class Wi-Fi anytime, anywhere.












































ElevenOS helps us deliver the Wi-Fi experience our customers expect. The login process is guest-friendly, back-end administration can be done at the brand or property level, and the front desk staff doesn’t have to spend time troubleshooting. It just works.

We selected ElevenOS to go beyond just delivering premium Wi-Fi automatically to our Hello Rewards members. We are excited to enable Wi-Fi driven services that create personalized guest experiences and deliver revenue opportunities for our owners.

ElevenOS provides a central dashboard where front desk managers can easily set up access codes and create portals with real-time analytics. Guest complaints have been reduced to virtually zero and our IT team can focus on other priorities. We are very happy with the solution.

Integrate with your existing hardware and software. Perfect your Wi-Fi configuration with detailed analysis. Scale and manage Wi-Fi performance across multiple properties. Handle daily operations through our intuitive dashboard, enable non-technical staff to skip the IT desk, free up resources and reduce operating costs.
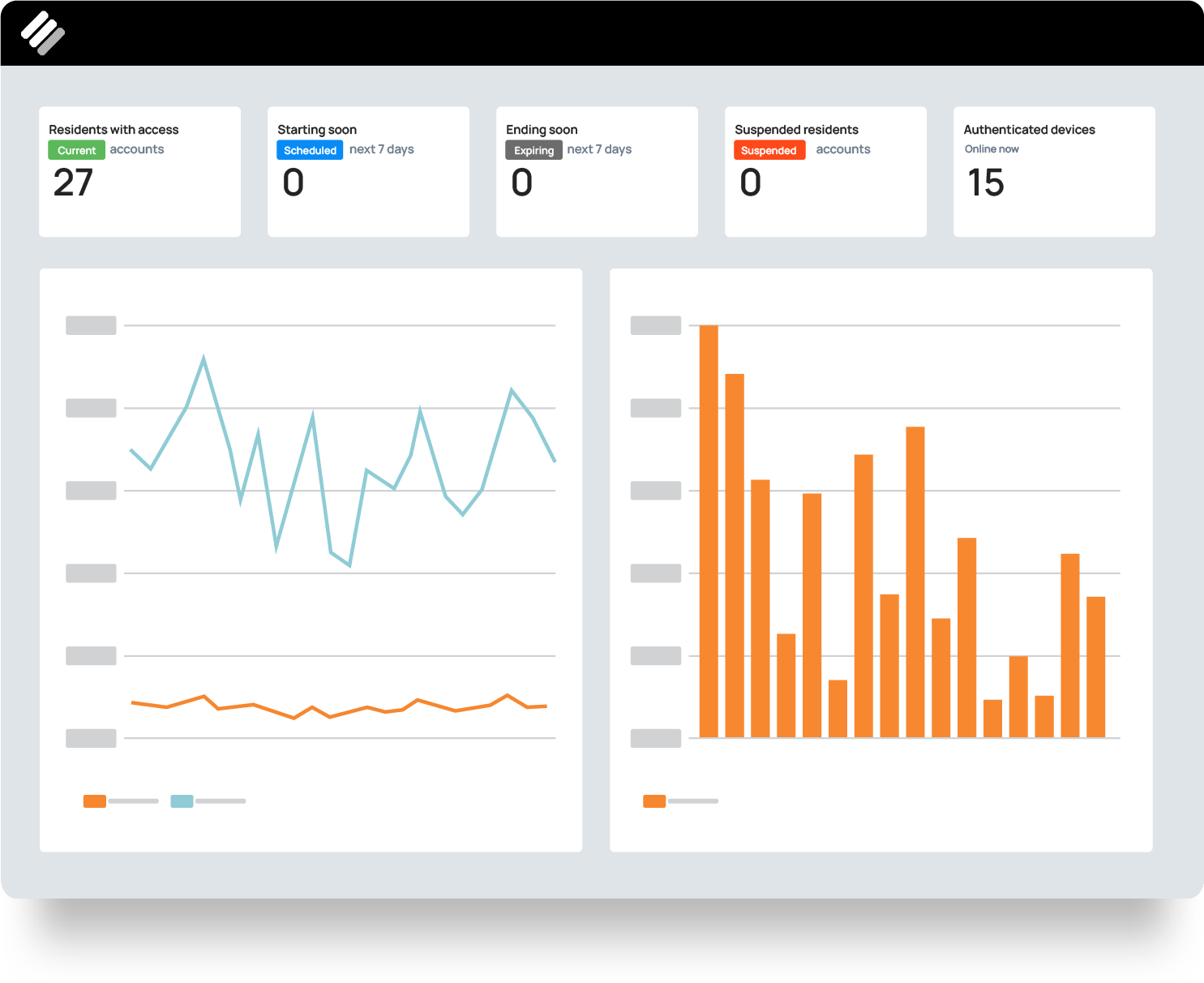
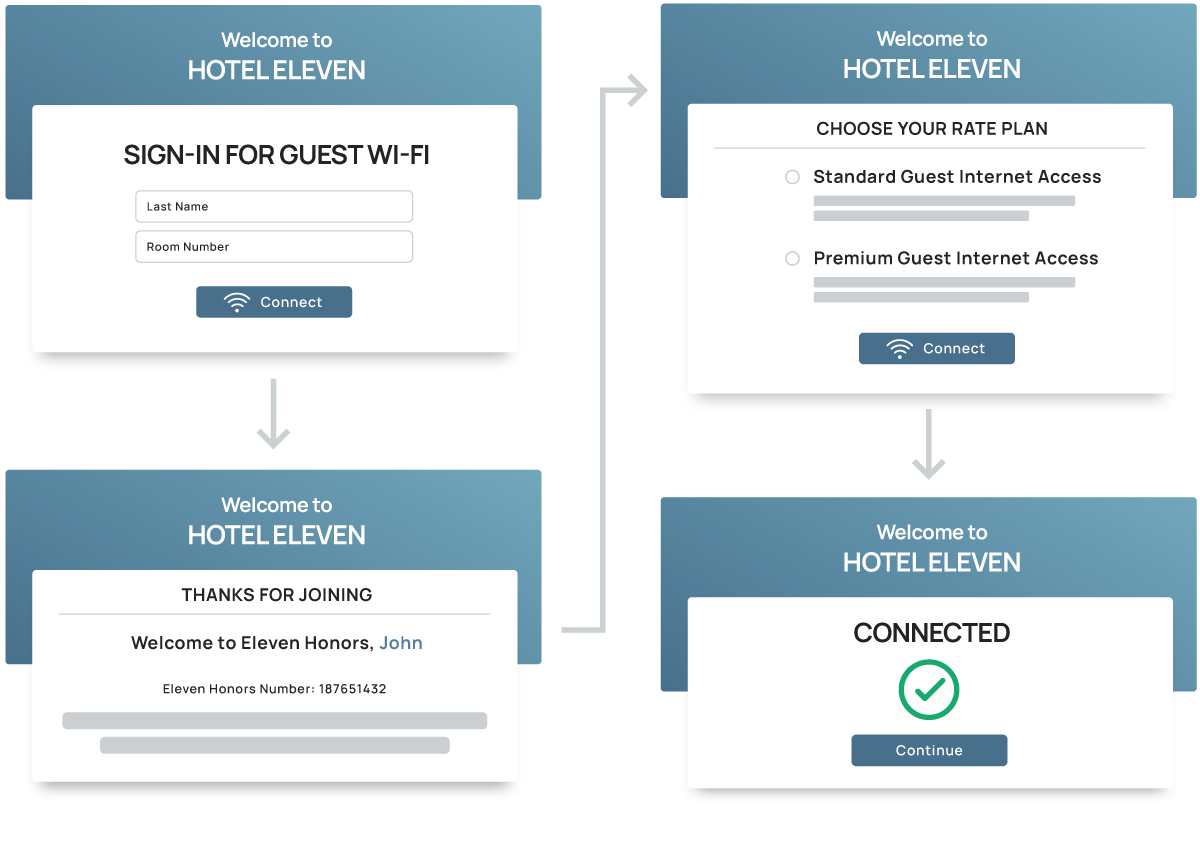
Bulk Wi-Fi becomes a revenue center with tiered network access. Connect ElevenOS to your loyalty program, configure pricing tiers, cap bandwidth, and roll it all into a seamless onboarding experience that delights guests and residents. From property to property, your brand delivers a consistent connectivity experience.





